Publications
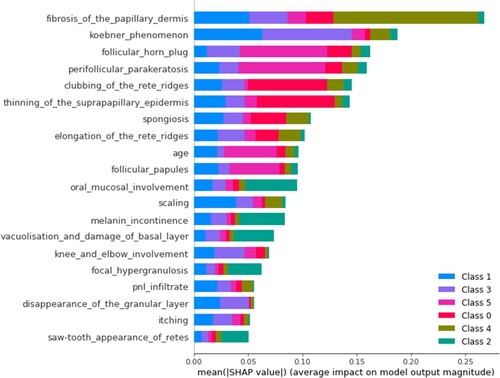
Erythemato-Squamous Diseases Prediction and Interpretation Using Explainable AI
Diagnosing erythemato-squamous diseases (ESD) is challenging in dermatology, with six main categories. This study applies Random Forest and XGBoost models to a standard dataset, using SHAP values to interpret model decisions and enhance transparency. The Random Forest model achieved 98.21% accuracy, while explainability tools identified disease root causes, improving trust and addressing ethical concerns like transparency and interpretability in AI-driven healthcare.
Paper | IETE Journal of Research | Q3
Customer Purchasing Behavior Prediction Using Machine Learning Classification Techniques
Many sales and service companies target existing customers to promote new products and updates, analyzing purchasing behavior to refine sales strategies. This paper compares machine learning models for predicting customer behavior, including methods like logistic regression, decision trees, KNN, SVM, random forest, and ensemble hybrids (e.g., SvmAda, RfAda, KnnSgd). Models were assessed via cross-validation, with confusion matrix and ROC curve analysis. The top-performing model, KnnSgd, achieved 92.42% accuracy by minimizing KNN and SGD errors through stacking.
Paper | Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing | Q1
Developing an Explainable Machine Learning-Based Thyroid Disease Prediction Model
Machine learning is widely used in healthcare, but many models lack transparency, leading to black-box systems that can limit trust and adoption in medical settings. This work focuses on an explainable thyroid disease diagnosis system, using SHAP—a game theory-based interpretability method—to clarify model behavior both locally and globally. By highlighting feature importance and model insights, this approach supports doctors in understanding disease causality and selecting effective treatments, enhancing system reliability and social acceptability.
Paper | IJBAN | Q4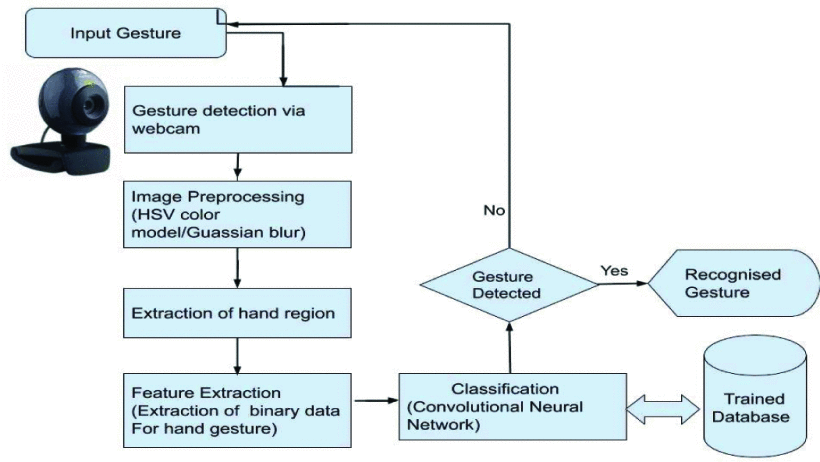
Hand Gesture Identification System Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Hand movement recognition is essential in advancing human-machine interaction, with applications like sign language interpretation. This paper presents a practical approach to hand gesture detection using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Key stages include data acquisition, pre-processing, segmentation, feature extraction, and classification, with a discussion on algorithms, their advantages, challenges, and limitations. This method, tested on 8,700 images, achieved over 95% classification accuracy. The best-performing model, KnnSgd, reached 92.42% accuracy by reducing KNN and SGD errors through stacking, supporting future research in gesture recognition.
Paper | IEEE Xplore | AIMV'21 | Conf. Paper
Personality Prediction Through Handwriting Analysis Using Convolutional Neural Networks
The prediction of personality traits through handwriting analysis is done by the Graphologist. The famous methodology of doing this analysis is commonly known as graphology. The prediction of personality traits using handwriting depends upon how much the graphologist is efficient in doing so. The development of computer-based handwriting analysis algorithm can make a great impact in predicting personality traits. In this paper, convolutional neural network (CNN) is used to predict the five big personality traits (Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Neuroticism, Openness) of the writer at the time of writing.
Paper | ICCI 2020 | Book Chapter
Hjorth Parameter based Seizure Diagnosis using Cluster Analysis
The rise in health issues over recent years has increased the demand for advanced healthcare tools to assist doctors in intelligent patient care. Biomedical signals, particularly from the brain, provide valuable insights but are difficult for non-experts to interpret. Epilepsy, affecting around 50 million people worldwide, manifests as abnormal neural activity and seizures. This paper proposes an advanced diagnostic approach using clustering algorithms to classify EEG data into normal and epileptic states by extracting Hjorth parameters. Among k-means, BSAS, PAM, FCM, and Valley-Seeking algorithms, Valley-Seeking achieved the highest accuracy at 87% for seizure detection.
Paper | Journal of Physics: Conf. Series | Q4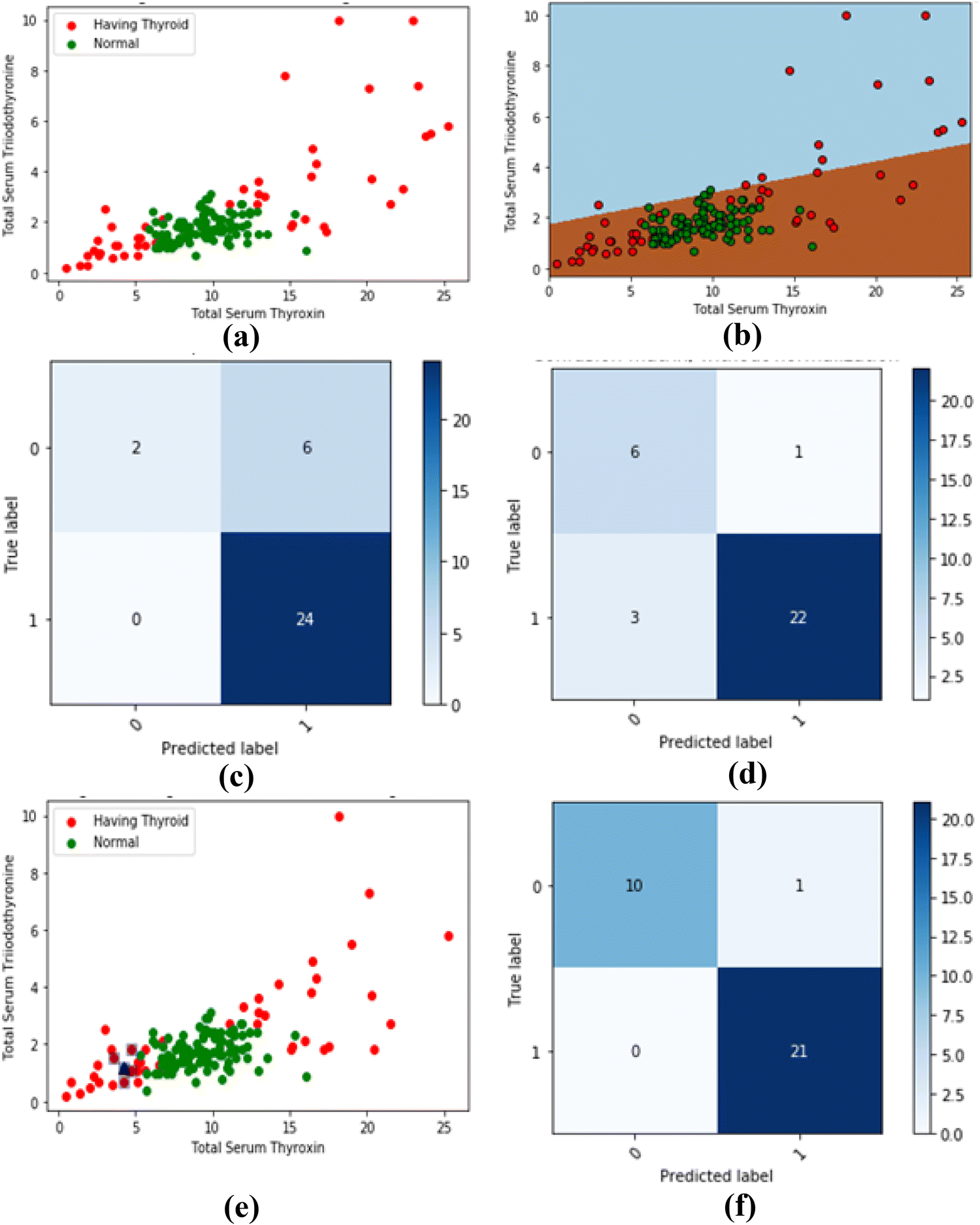
Thyroid Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning Approaches
This paper is being written to provide a source of reference for the research scholars who want to work in the area of prediction of thyroid disease. From the different machine learning techniques, compared widely used three algorithms namely logistic regression, decision trees and k-nearest neighbor (kNN) algorithms to predict and evaluate their performance in terms of accuracy. This study has represented the intuition of how to predict the thyroid disease and highlighted how to apply the logistic regression, decision trees and kNN as a tool for the classification. For this, thyroid data set of machine learning repository has used from UC Irvin knowledge discovery in databases archive.
Paper | National Academy of Science Letters | Q3